- Product Details
Keywords
- Capecitabine supplier
- Capecitabine China
- Capecitabine 98%
Quick Details
- ProName: Capecitabine 98% supplier in China
- CasNo: 154361-50-9
- Molecular Formula: C15H22FN3O6
- Appearance: powder
- Application: API
- PackAge: 7.5KG
- Port: shanghai
- ProductionCapacity: Metric Ton/Day
- Purity: 98%
- Storage: Room temperature
- Transportation: by air or by sea
- LimitNum: 0 Metric Ton
Superiority
High quality product, competitive price and best service.
Details
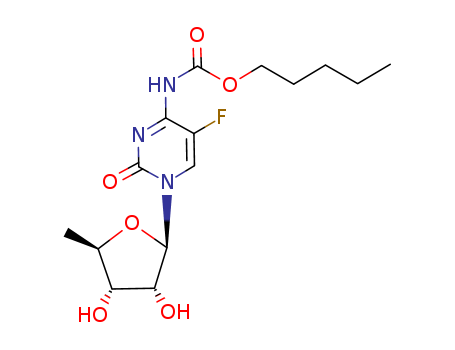
1.Introduction of Capecitabine
The Capecitabine, with the CAS registry number 154361-50-9, is also known as N(4)-Pentyloxycarbonyl-5'-deoxy-5-fluorocytidine. It belongs to the product categories of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients; Antineoplastic; Bases & Related Reagents; Intermediates & Fine Chemicals; Nucleotides; Pharmaceuticals; Antineoplastic drug, 5-FU analog; Anti-cancer. This chemical's molecular formula is C15H22FN3O6 and molecular weight is 359.35. What's more, its systematic name is 5'-Deoxy-5-fluoro-N-
[(pentyloxy)carbonyl]cytidine. Its classification codes are: (1)Antimetabolites; (2)Antimetabolites, Antineoplastic; (3)Antineoplastic; (4)Antineoplastic agents; (5)Noxae. This chemical is an orally-administered chemotherapeutic agent used in the treatment of metastatic breast and colorectal cancers. Capecitabine is a prodrug of doxifluridine and an antineoplastic agent , that is enzymatically converted to fluorouracil (antimetabolite) in the tumor, where it inhibits DNA synthesis and slows growth of tumor tissue.
2.Physical properties of Capecitabine
(1)ACD/LogP: 1.042; (2)# of Rule of 5 Violations: 0; (3)ACD/LogD (pH 5.5): 0.76; (4)ACD/LogD (pH 7.4): -0.60; (5)ACD/BCF (pH 5.5): 1.89; (6)ACD/BCF (pH 7.4): 1.00; (7)ACD/KOC (pH 5.5): 45.62; (8)ACD/KOC (pH 7.4): 2.02; (9)#H bond acceptors: 9; (10)#H bond donors: 3; (11)#Freely Rotating Bonds: 8; (12)Polar Surface Area: 120.69 ?2; (13)Index of Refraction: 1.6; (14)Molar Refractivity: 82.327 cm3; (15)Molar Volume: 240.522 cm3; (16)Polarizability: 32.637 10-24cm3; (17)Surface Tension: 51.3009986877441 dyne/cm; (18)Density: 1.494 g/cm3.
3.Structure of Capecitabine
(1)SMILES: FC=1\C(=N/C(=O)N(C=1)[C@@H]2O[C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@H]2O)C)\N
C(=O)OCCCCC
(2)Std. InChI: InChI=1S/C15H22FN3O6/c1-3-4-5-6-24-15(23)18-12-9(16)7-19(14(22)17-12)13-
11(21)10(20)8(2)25-13/h7-8,10-11,13,20-21H,3-6H2,1-2H3,(H,17,18,22,23)/t8-,10-,11-,13-/m1/s1
(3)Std. InChIKey: GAGWJHPBXLXJQN-UORFTKCHSA-N
4.Pharmacodynamics of Capecitabine
it is a fluoropyrimidine carbamate with antineoplastic activity indicated for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer and colon cancer. It is an orally administered systemic prodrug that has little pharmacologic activity until it is converted to fluorouracil by enzymes that are expressed in higher concentrations in many tumors. Fluorouracil it then metabolized both normal and tumor cells to 5-fluoro-2’-deoxyuridine 5’-monophosphate (FdUMP) and 5-fluorouridine triphosphate (FUTP).
5.Mechanism of action of Capecitabine
Capecitabine is a prodrug that is selectively tumour-activated to its cytotoxic moiety, fluorouracil, by thymidine phosphorylase, an enzyme found in higher concentrations in many tumors compared to normal tissues or plasma. Fluorouracil is further metabolized to two active metabolites, 5-fluoro-2'-deoxyuridine 5'-monophosphate (FdUMP) and 5-fluorouridine triphosphate (FUTP), within normal and tumour cells. These metabolites cause cell injury by two different mechanisms. First, FdUMP and the folate cofactor, N5-10-methylenetetrahydrofolate, bind to thymidylate synthase (TS) to form a covalently bound ternary complex. This binding inhibits the formation of thymidylate from 2'-deaxyuridylate. Thymidylate is the necessary precursor of thymidine triphosphate, which is essential for the synthesis of DNA, therefore a deficiency of this compound can inhibit cell division. Secondly, nuclear transcriptional enzymes can mistakenly incorporate FUTP in place of uridine triphosphate (UTP) during the synthesis of RNA. This metabolic error can interfere with RNA processing and protein synthesis through the production of fraudulent RNA.