- Product Details
Keywords
- 4-Hydroxycoumarin supplier
- 4-Hydroxycoumarin China
- 4-Hydroxycoumarin 98%
Quick Details
- ProName: 4-Hydroxycoumarin 98% supplier in Chin...
- CasNo: 1076-38-6
- Molecular Formula: C9H6O3
- Appearance: white to off-white powder
- Application: intermediates
- PackAge: 25kg/drum
- Port: shanghai
- ProductionCapacity: Metric Ton/Day
- Purity: 98%
- Storage: storage in shady and cool warehouse
- Transportation: by air or by sea
- LimitNum: 1 Kilogram
Superiority
we have 3 OEM factories, 2 R&D labs. Aily is striving to improve reseach and development, meet social and customers needs with a unifying strategic idea.
Details
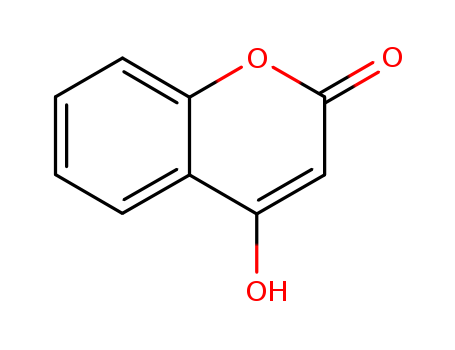
1. Introduction of 4-Hydroxycoumarin
The 4-Hydroxycoumarins are a class of vitamin K antagonist (VKA) anticoagulant drug molecules derived from coumarin (chromen-2-one) by adding a hydroxy group at the 4 position to obtain "4-hydroxycoumarin" (or "4-hydroxychromen-2-one"; formally then renumbered as 2-hydroxychromen-4-one), then adding a large aromatic substituent at the 3-position (the ring-carbon between the hydroxyl and the carbonyl). The large 3-position substituent is required for anticoagulant activity.
2. Properties of 4-Hydroxycoumarin
Molecular Weight 162.14214 [g/mol]
Molecular Formula C9H6O3
XLogP3-AA 1.3
H-Bond Donor 1
H-Bond Acceptor 3
Tautomer Count 3
Exact Mass 162.031694
MonoIsotopic Mass 162.031694
Topological Polar Surface Area 46.5
Heavy Atom Count 12
Complexity 232
Covalently-Bonded Unit Count 1
Feature 3D Acceptor Count 1
Feature 3D Donor Count 1
Feature 3D Ring Count 2
Conformer Sampling RMSD 0.4
CID Conformer Count 1
3. Structure descriptors of 4-Hydroxycoumarin
IUPAC Name: 4-hydroxychromen-2-one
InChI: InChI=1S/C9H6O3/c10-7-5-9(11)12-8-4-2-1-3-6(7)8/h1-5,10H
InChIKey: VXIXUWQIVKSKSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Canonical SMILES : C1=CC=C2C(=C1)C(=CC(=O)O2)O
4. Application of 4-Hydroxycoumarin
The synthetic drugs in the 4-hydroxycoumarin class are all noted primarily for their use as anticoagulants, though they can have several additional effects. All affect the normal metabolism of vitamin K in the body by inhibiting the enzyme vitamin K epoxide reductase which recycles vitamin K to active form. As such, these compounds form the most important and widely used subset of vitamin K antagonist drugs, but other such drugs exist which do not have the 4-hydroxycoumarin structure. All the vitamin K antagonist agents diminish the amount of available vitamin K in the body, and thus inhibit the action of vitamin K-dependent enzymes that are critically involved in the production of active forms of certain clotting factors, and certain other metabolic processes involving the binding of calcium ion.