- Product Details
Keywords
- Indene supplier
- Indene China
- Indene 98%
Quick Details
- ProName: Indene 98% supplier in China
- CasNo: 95-13-6
- Molecular Formula: C9H8
- Appearance: Colorless or light yellow transparent ...
- Application: fine chemical
- PackAge: 180kg/drum
- Port: shanghai
- ProductionCapacity: Metric Ton/Day
- Purity: 98%
- Storage: Room temperature
- Transportation: by air or by sea
- LimitNum: 1 Metric Ton
Superiority
we have 3 OEM factories, 2 R&D labs. Aily is striving to improve reseach and development, meet social and customers needs with a unifying strategic idea.
Details
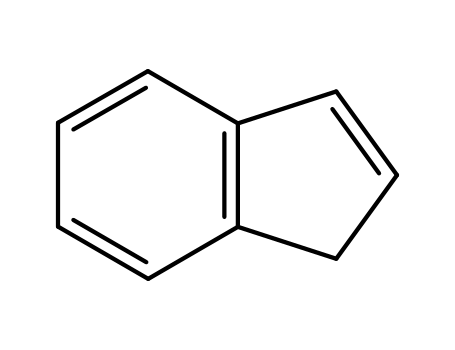
1. Introduction of Indene
The Indene, with its CAS NO 95-13-6, is a kind of Colorless or light yellow transparent liquid. It has synonyms of 1H-Indene;HSDB 5286;Inden;Indonaphthene and NSC 9270. Indene is a flammable polycyclic hydrocarbon with chemical formula C9H8. It is composed of a benzene ring fused with a cyclopentene ring. This aromatic liquid is colorless although samples often are pale yellow. The principal industrial use of indene is in the production of indene/coumarone thermoplastic resins.
2. Properties of Indene
ACD/LogP: 3.043 ACD/LogD (pH 5.5): 3.04 ACD/LogD (pH 7.4): 3.04
ACD/BCF (pH 5.5): 121.05 ACD/BCF (pH 7.4): 121.05
ACD/KOC (pH 5.5): 1077.94 ACD/KOC (pH 7.4): 1077.94
#Freely Rotating Bonds: 0 Polar Surface Area: 0 ?2
Index of Refraction: 1.596 Molar Refractivity: 38.031 cm3
Molar Volume: 111.818 cm3 Polarizability: 15.077 10-24cm3
Surface Tension: 42.1269989013672 dyne/cm Density: 1.039 g/cm3
Flash Point: 58.889 °C Enthalpy of Vaporization: 40.072 kJ/mol
Boiling Point: 181.599 °C at 760 mmHg Vapour Pressure: 1.14999997615814 mmHg at 25°C
3. Isolation
Indene occurs naturally in coal-tar fractions boiling around 175–185 °C. It can be obtained by heating this fraction with sodium to precipitate solid "sodio-indene." This step exploits indene's weak acidity evidenced by its deprotonation by sodium to give the indenyl derivative. The sodio-indene is converted back to indene by steam distillation.
4. Reactivity
Indene readily polymerises. Oxidation of indene with acid dichromate yields homophthalic acid (o-carboxylphenylacetic acid). It condenses with ethyl oxalate in the presence of sodium ethoxide to form indene-oxalic ester, and with aldehydes or ketones in the presence of alkali to form benzofulvenes. The latter are highly coloured. An indene is also a precursor to the indenyl anion, a ligand in organometallic chemistry with some notability due to the indenyl effect.